Investigators:
Gang Wang, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Roopa Foulger and Jonathan A. Handler, OSF
MassAITC Cohort: Year 3 (Aging)
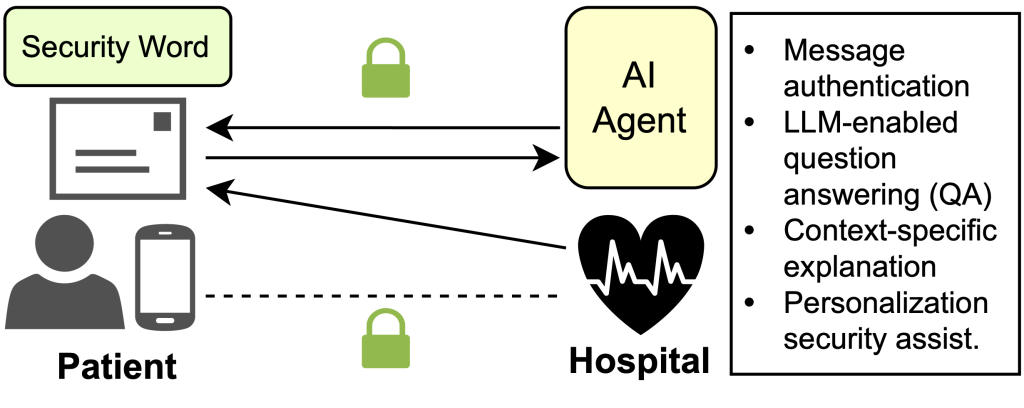
Project Accomplishments: The UIUC pilot project focused on developing SmishX, an AI‑enabled agent designed to help users—especially older adults—detect and understand phishing attempts delivered via SMS. Over the course of the project (2024–2026), the team built a functional prototype capable of evaluating message intent, gathering contextual information (such as URL resolution and web screenshots), and generating both concise and detailed explanations for users. After securing IRB approval and establishingstudy infrastructure, the system was evaluated on a curated dataset of 1,200 SMS messages, achieving 98.9% accuracy and outperforming existing machine‑learning and LLM‑based baselines. The team then conducted a large-scale user study with 175 participants (including 70 older adults), demonstrating that SmishX significantly improves phishing‑detection performance and is rated “excellent” in usability.
A follow‑up study with 240 additional participants explored how users respond to AI errors and disagreements, leading to a new model that estimates when AI‑assisted decision-making yields a net positive effect on phishing defense. By late 2025, OSF Healthcare implemented SmishX as a locally hosted internal web service, marking a key translational milestone. Additionaloutcomes included a labeled phishing dataset, refined explainability methods, and strengthened partnerships across research and healthcare communities.
Initial Proposal Abstract: This project aims to design, prototype, evaluate, and potentially deploy an AI-enabled voice agent to assist patients (especially older adults) to better recognize phishing messages and reduce cybersecurity risks during patient outreach and communications.
Timely patient outreach and communication are critical to the well-being of patients and improve the efficiency of healthcare workers. Without security measures, such communication channels are vulnerable to phishing attacks (where malicious hackers trick the victims into revealing sensitive information). To help patients better recognize phishing messages and verify message authenticity, we propose to design and develop AI-enabled voice agents. The system includes (1) a security-word-based message verification scheme to verify message authenticity, and (2) an AI agent powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) to help patients with little to no technical background to recognize phishing attempts (based on signals including the security words) and take safe actions.
To evaluate the effectiveness and usability of the system, we plan to recruit 52 participants (including older adults) to interact with the voice agent and perform phishing detection tasks. We will collect both quantitative and qualitative data to assess and further improve the system. We will work with OSF Healthcare to explore deployment opportunities.
Outcomes:
- Publication: Proceedings from SOUPS ’25 – Can You Walk Me Through It? Explainable SMS Phishing Detection using LLM-based Agents
 Authors: Yizhu Wang, Haoyu Zhai, Chenkai Wang, Qingying Hao, Nick A Cohen, Roopa Foulger, Jonathan A Handler, and Gang Wang. Abstract SMS phishing poses a significant threat to users, especially older adults. Existing defenses mainly focus on phishing detection, but often cannot explain why the SMS is malicious to lay users. In… Read more: Publication: Proceedings from SOUPS ’25 – Can You Walk Me Through It? Explainable SMS Phishing Detection using LLM-based Agents
Authors: Yizhu Wang, Haoyu Zhai, Chenkai Wang, Qingying Hao, Nick A Cohen, Roopa Foulger, Jonathan A Handler, and Gang Wang. Abstract SMS phishing poses a significant threat to users, especially older adults. Existing defenses mainly focus on phishing detection, but often cannot explain why the SMS is malicious to lay users. In… Read more: Publication: Proceedings from SOUPS ’25 – Can You Walk Me Through It? Explainable SMS Phishing Detection using LLM-based Agents - Poster Presentation: a2 National Symposium 2025
 Title: Protecting Patients against Phishing Attacks using AI-enabled Agents Authors: Yizhu Wang, Haoyu Zhai, Chenkai Wang, Qingying Hao, Nick Cohen, Roopa Foulger, Jon Handler, Gang Wang
Title: Protecting Patients against Phishing Attacks using AI-enabled Agents Authors: Yizhu Wang, Haoyu Zhai, Chenkai Wang, Qingying Hao, Nick Cohen, Roopa Foulger, Jon Handler, Gang Wang - Oral Presentation: Mobile Computing Seminar at Columbia University (Virtual)
 Dr. Gang Wang gave a virtual talk at Columbia University (mobile computing seminar) which highlighted this project and the prototype design. Title: Defending against Spoofing Attacks in Mobile Networks and Applications Presenter: Gang Wang (PI)
Dr. Gang Wang gave a virtual talk at Columbia University (mobile computing seminar) which highlighted this project and the prototype design. Title: Defending against Spoofing Attacks in Mobile Networks and Applications Presenter: Gang Wang (PI)
