Abstract
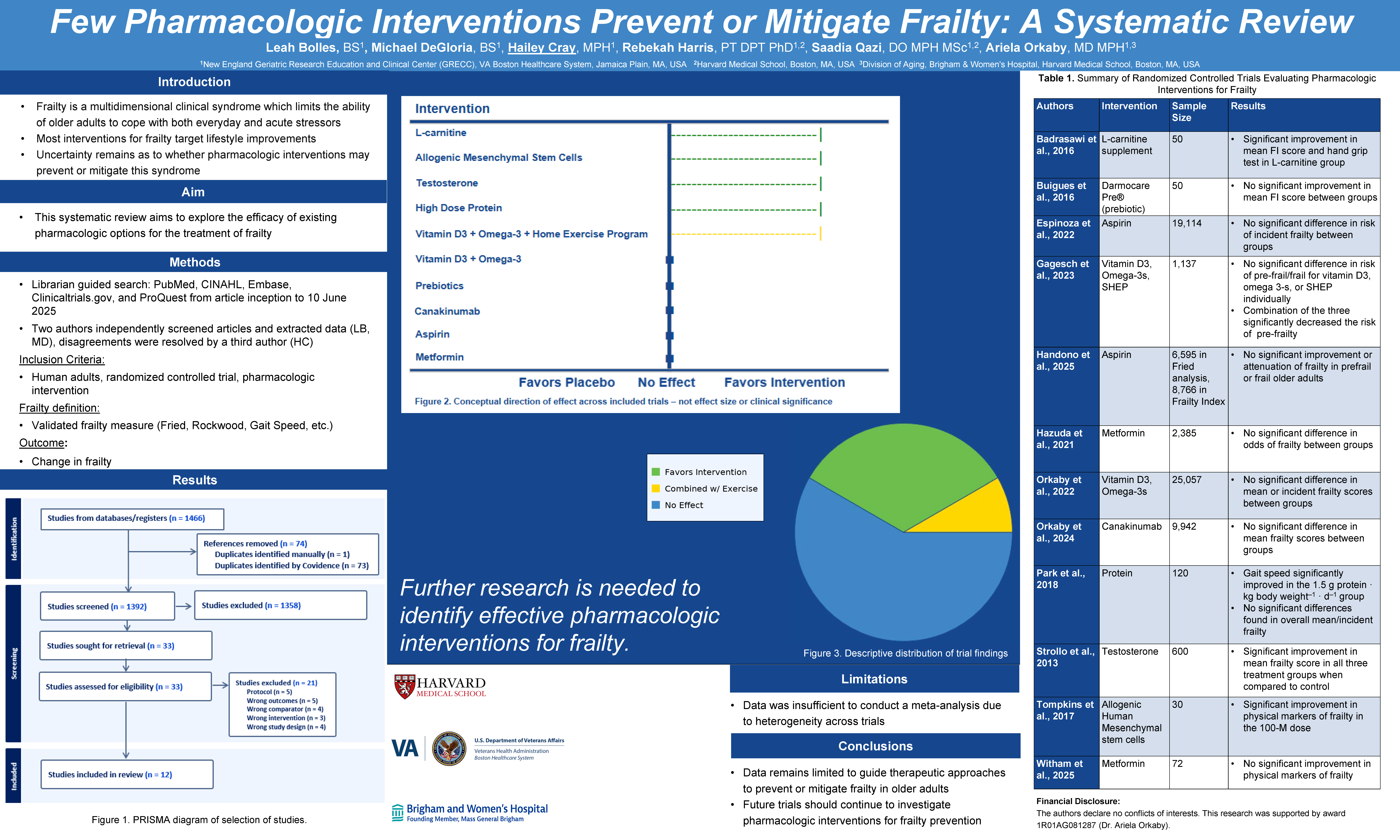
Frailty is a multidimensional clinical syndrome that limits the ability of older adults to cope with stressors. This systematic review explores the efficacy of pharmacologic options for treating frailty. Following PRISMA guidelines, we searched CINAHL, Embase, ProQuest Health and Medical, and PubMed up to 4 September 2025. Only randomized controlled trials evaluating pharmacologic interventions on validated frailty measures were included. After screening 1392 titles, 12 trials were included. L-carnitine, high-dose protein supplementation, testosterone therapy, and intravenous mesenchymal stem cells show promise. Other interventions showed no reduction in frailty. Data were insufficient for a meta-analysis. More research is needed to guide therapeutic approaches.