Investigators:
Dave Keeley, Electronic Caregiver, Inc.
Michael Busa, UMass Amherst
MassAITC Cohort: Year 2 (AD/ADRD)
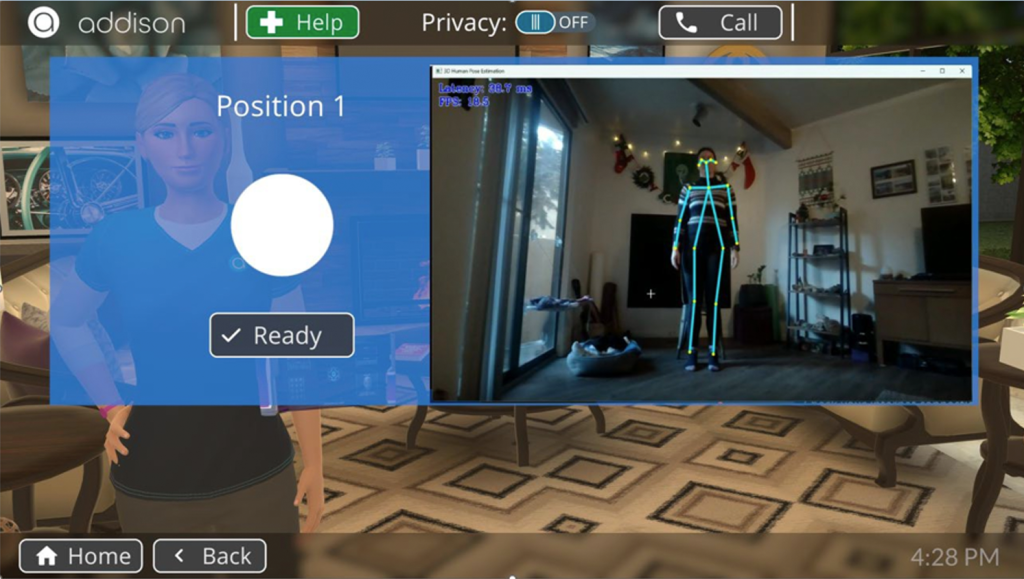
Initial Proposal Abstract: Falls are a major cause of injury and death in older adults. Annually, over 25% of Americans aged 65+ experience a fall, resulting in 3 million patients being treated in a hospital for fall related injuries and thousands of premature deaths. Moreover, the cost of falls to the health care system exceeds $50 billion annually1. Elderly with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Alzheimer’s Disease Related Dementia (ADRD) have a double to threefold increased risk for the occurrence of falls.
Electronic Caregiver, Inc. (ECG) is a telehealth technology and services company providing hospital-at-home and aging-in-place solutions to over 250,000 older adults and care teams to improve independence, proactively inform providers of changes in health conditions, and lower health care costs. Addison Care is ECG’s care-at-home product used to provide reminders, track medication compliance, obtain vital sign measurements, deliver care plan assessments, and monitor ADLs.
The intent of this research project is to augment this existing information with data obtained via the system’s camera to evaluate functional strength, stability, and falls risk. Traditionally, such evaluations are done annually in a clinical setting. Addison Care can complement an annual assessment of falls risk with on-demand, remote assessment in a patient’s home. This new data – coupled with the information already obtained via the Addison Care system – would be used to create a new “Falls Prevention” module for commercialization and licensing.
The ability to provide clinical-level assessments of functional strength and incorporate this data into a comprehensive home-based falls risk assessment tool would be significant, especially in the case of AD/ADRD patients, as rate of disease progression can vary widely. Worsening of symptoms that affect perception, balance, and vision dramatically increase falls risk. This creates an opportunity to proactively identify real-time risk factors and changes to functional strength which can trigger falls. Preventing 10% of major falls in the US would reduce ER visits by 300,000, save $5B in health care costs, and reduce preventable deaths – annually.
Outcomes:
- Poster Presentation: a2 National Symposium 2024
 Title: Decreasing Risk of Falls via Computer Vision & AI Driven Functional Assessments Authors: David Keeley, Michael Bush, Corinna Serviente, Marissa Graham, Bailey Henderson
Title: Decreasing Risk of Falls via Computer Vision & AI Driven Functional Assessments Authors: David Keeley, Michael Bush, Corinna Serviente, Marissa Graham, Bailey Henderson - Award: 2022 Inc 5000 Fastest Growing Private Companies in America
 Among their 2022 Awardees, Inc 5000 listed Electronic Caregiver as #969 among the fastest growing private companies in America Source: https://www.inc.com/inc5000/2022#
Among their 2022 Awardees, Inc 5000 listed Electronic Caregiver as #969 among the fastest growing private companies in America Source: https://www.inc.com/inc5000/2022#
